
Do you wonder why our elders always keep emphasizing on eating raw and natural foods instead of junk? That lies in the nutritional and beneficial capacity these plant and animal materials have for the strength of our bodies. All the components of our natural eatables have their own specific role in this regard. Vitamin A, the retinol family is abundant in animal foods. These include liver, kidney, egg-yolk, milk, cheese, butter, fish oils especially cod and shark liver oils. The provitamin forms also called carotenes are of plant origin which include green vegetables i.e. spinach, carrots, pumpkins, mango.
Some 3600 years ago, Hippocrates used this vitamin to treat night blindness by the formulation of ox liver in honey hinting at its animal source. The lipophilic character of vitamin A allows its absorption in the small intestine along with fats. It is processed and stored in the liver and is released in the plasma as per requirement. Following points give the track of some major functions vitamin A plays in one’s body.
1. Normal Vision/ Color Vision: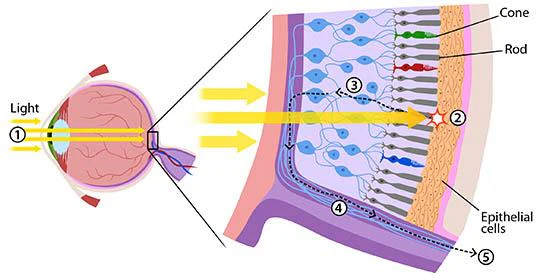
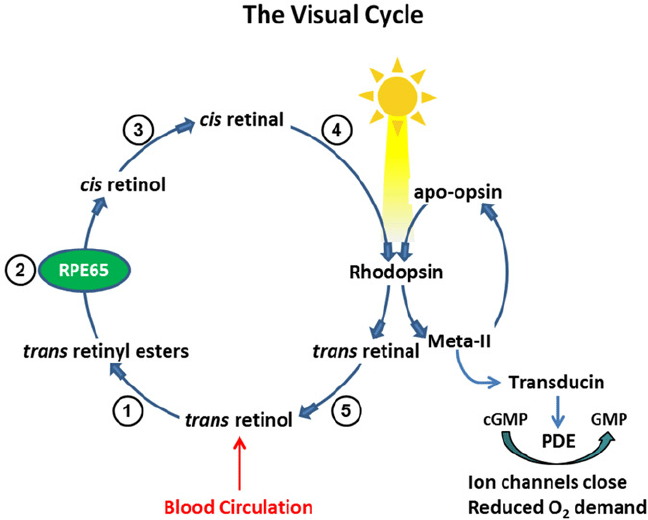
Let’s get into the science of how carrots are beneficial for sharp sight. The photoreceptive layer of the retina contains a pigment “rhodopsin” within the rod cells. Rhodopsin is composed of retinal (the aldehyde form of vitamin A) and the protein opsin. When light falls on the retina of the eye, the rhodopsin bleaches off and splits. The signal is transduced to the brain and it processes the image. However, regeneration of rhodopsin requires retinol supplied from diet which if deficient may affect vision. Such people when shifted from a bright room to a dim one (i.e. cine theatre) experience a prolonged delay in dark adaptation.
Cone cells, coexistent with rods within the retina, contain the pigment “iodopsin” and work on the same principle. However, the three types of cones for each of the three primary colors red, blue, and green detect their own specific color.
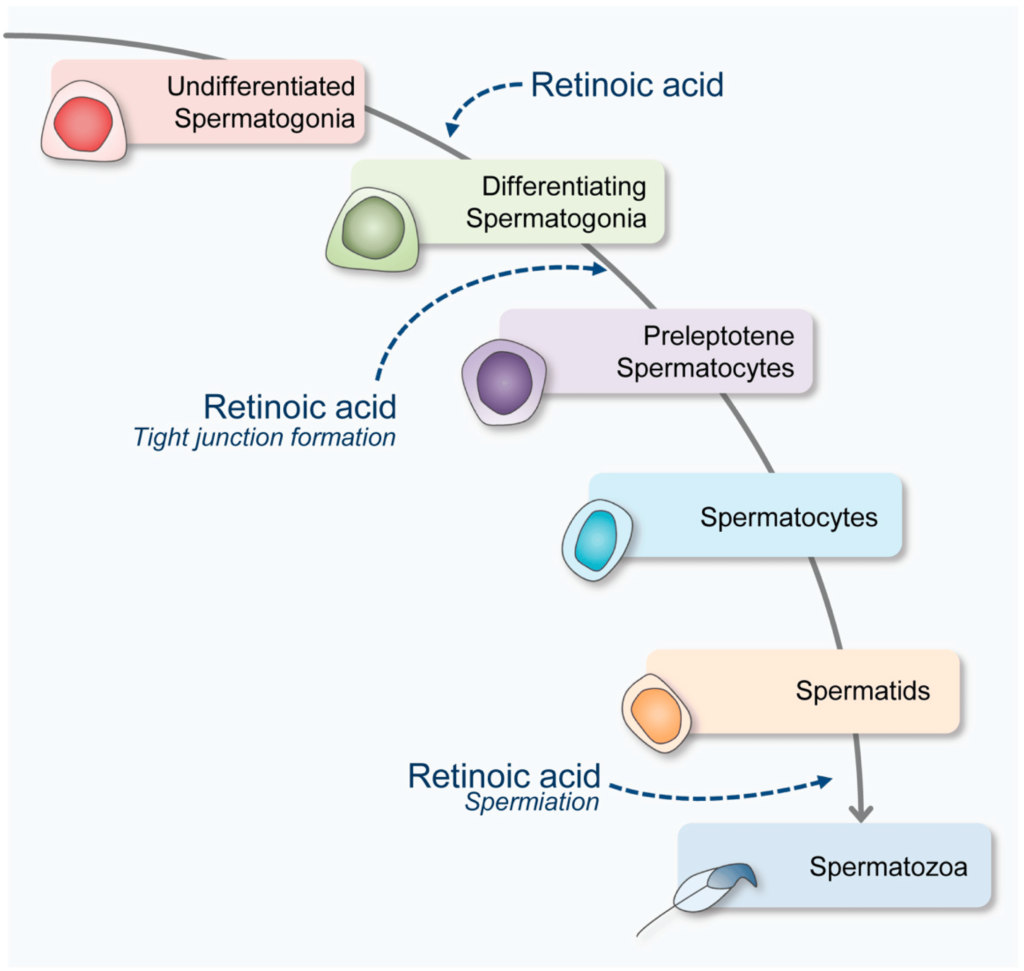
2. Normal Reproduction:
Retinol is essential for normal reproduction, activating spermatogenesis in males but preventing fetal resorption in addition to promoting placental growth and embryonic development. Retinol as a component of Cellular Retinol Binding Protein (CRBP) brings about gene expression thus acting as steroid hormone in reproduction. Deficiency may lead to sterility due to degeneration of germinal epithelium in males and early termination of pregnancy in females.
3. Glycoprotein synthesis:
Retinoic acid in phosphate serves as an oligosaccharide carrier in the synthesis of glycoproteins and thus aids normal growth. The chondroitin SO4 synthesized by vitamin A also forms the major part of ground substance of epithelial tissues as mucopolysaccharides. Deficiency may present with cell growth retardation, diminished cell differentiation and impairment in skeletal formation.
4. Immune Function:
The provitamin form of vitamin A, beta carotenes perform their antioxidant activity by trapping the peroxy radicals in tissues at low partial pressure of O2. The free radicals have the ability to form cancers in the body. Thus the protective role of vitamin A saves the body from the toxic effects of free radicals getting the title of “anti-infective vitamin”. The maintenance of proper immune system is also a function of vitamin A which helps fight against various infections.
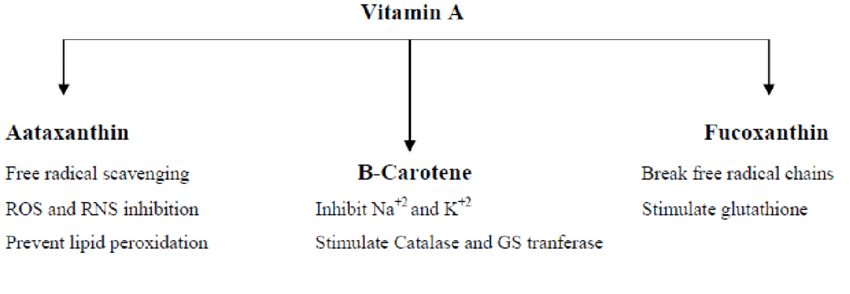
5. Healthy Epithelium:
Epithelial nourishment is specifically attributed as the corollary of vitamin A activity. This is due to the fact that vitamin A has a direct role in the control of keratin synthesis preventing dry skin under normal conditions. However, lack of dietary availability and depletion of body stores of vitamin A leads to keratinization of epithelium of urinary, gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts. As a result, the person becomes prone to urinary stone formation and bacterial infections. The skin also becomes rough, dry and scaly.
Recommended Daily Allowance:
Daily requirement of vitamin A expressed as Retinol Activity Equivalent (RAE) is around 1000 RAE for adult males and 800 RAE for adult females. The requirement increases in pregnancy, lactation and in growing children.
Hypervitaminosis may also adversely affect health causing dermatitis, liver enlargement, skeletal decalcification, anorexia, hair loss and joint pain. Thus a neutral amount is lucrative to health.