
Proteins, also termed as building blocks of the body, are the most important structures forming cells and tissues. They are composed of long chains of amino acids that are about 20 in number. Of these, only 10 are normally synthesized in our bodies through translation and are termed as non essential amino acids. The ten essential amino acids that are required for cell functioning are obtained through food sources. The arrangement of these amino acids decide the structure and functions of proteins. Thus, these polypeptides play roles as hormones, enzymes, clotting factors, defensins, transporters etc. along with being the structural components of membranes and plasma.
Exceptional functions of proteins
Some of the exceptional functions of proteins include their capability of conversion to fats and carbohydrates thus providing energy. In addition, transport and supply of oxygen to all the tissues of body is under control of hemoglobin and myoglobin. Some of the enzymes have diagnostic roles in laboratory for disease detection. Plasma proteins also regulate fluid levels of the body. Furthermore, tissue repair and wound healing is also attributed to the working of proteins. As collagen and other fibrillar proteins, they provide tensile strength to bones and muscles. Enzymes also regulate the metabolic functions of the body.
Fat and Carbs replacement
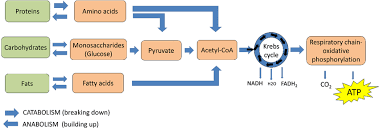
Proteins are interconvertible to other macronutrients thus playing roles in energy provision and weight management. Amino acids- alanine, serine, glycine, cystine, threonine are termed as glucogenic amino acids as they are convertible to pyruvate and thus can enter tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) to produce energy. Also, proteins, through deamination, can be converted to fatty acids for storage. Thus in the absence of these important macronutrients in diet, proteins can fill up some of the deficiency.
Oxygenation of the body
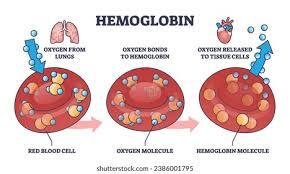
Myoglobin and hemoglobin are the two globin proteins responsible for oxygenation of the body. Hemoglobin transports whereas myoglobin stores oxygen. Hemoglobin has a capability of binding molecular oxygen and carrying it to the tissues from the lungs. At the destination, it drops off the oxygen (O2) and in turn binds carbon dioxide (CO2) thereby, removing this waste product from the body as well. Myoglobin or muscle hemoglobin binds oxygen with high affinity, only releasing it during aerobic glycolysis when a person is exercising. In addition, the blood sugar levels are measured efficiently by measuring the levels of a type of hemoglobin – HbA1c. HbA1c test provides information of a person’s glycemic index/ blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months. Thus, it is helpful for diagnosis of diabetes especially of Type 2.
Disease detection – role as enzymes

Proteins as enzymes also serve as biomarkers for several disease conditions in a person such as cancer, liver disease, kidney disease etc. Raised serum levels of enzymes such as Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) Creatine Kinase (CK) are indicative of liver, bone and muscle tissue damage. Also some laboratory diagnostic techniques involve the intermediation of enzymes. ELISA – Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is a procedure that uses an enzyme antibody complex to measure the levels of hormone, antibodies and antigens in blood. This is crucial for the detection for viral infections and other abnormal conditions due hormone imbalance.
pH and fluid balance
Plasma proteins especially, albumin, has the role of imbibition of water that helps regulate fluid levels of the body. Normally, this protein keeps the water in the bloodstream that helps with flow of nutrients and hormones to their target sites. However, in case of hypoproteinemia, Blood volume decreases as water enters the tissues causing edema and consequently blood pressure falls. Protuberant belly due to abdominal swelling is thus one of the most prominent symptom in people with kwashiorkor disease / protein malnourishment. As the colloid osmotic pressure falls, the homeostasis of the body is disturbed.

Tissue repair function of proteins
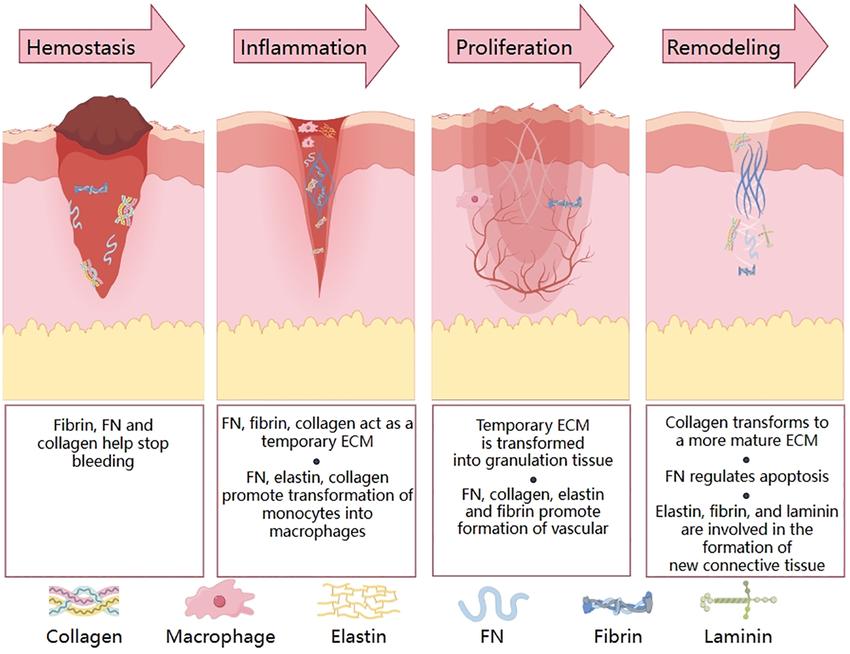
Damage or injury to any tissue calls for the activity of a number of proteins for the initiation of repair process. In this regard, fibrin clot is the first step in stopping bleeding. Next, all the component of connective framework like collagen, keratin, elastin provides the structural materials for filling up the damaged area. Consequently, the damaged tissue is cemented back to normal and the inflammation subsides. The processes of transcription and translation are also accelerated in case of excess tissue damage for the formation of new proteins. This occurs due to neuronal and hormonal regulation of homeostasis in the body.
Proteins as hormones
Various important hormones act as controllers of other hormones are protein in nature. These include
- Growth hormone
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
- Gonadotropic releasing hormone
- Insulin and Glucagon
- Oxytocin
All these have regulatory function in the body, maintaining growth, metabolism, stress response, sexual cycle, blood glucose levels and uterine contractions during labor respectively.
Proteins and Immunity
The most important component of immune system that fights any infection entering our body is an antibody. These antibodies or immunoglobulins are protein in nature and help engulf bacteria by attaching to it. Macrophages and other immune cells of the body recognize the invaders by these antibodies and kill them. Also, once an antibody ahs been formed in the body against a particular infectious agent, the memory of it is stored in the cells. Hence, boosting the immune system by strengthening it for future invasions.
Food sources of proteins
Fish, meats, poultry, eggs, milk, cheese, yoghurt, legumes, nuts, seeds are all rich sources of proteins. For vegans, quinoa, lentils, tofu, pulses and oats are recommended.