
Pantothenic acid also termed as ‘anti-stress vitamin’ and ‘anti gray hair factor’ is derived from a Greek word meaning ‘from everywhere. It belongs to the B complex category (called B5 vitamin) which serves as fuel generators converting the food to useful energy for the body. It can be synthesized by intestinal bacteria provided that its subunits pantoic acid and alanine are available.
Pantothenic acid has a bunch of functional capabilities fulfilling its role in energy yielding, fat synthesis, heme synthesis, nervous function, protein metabolism, stress hormones synthesis from adrenal glands, blood cell production etc. The cosmetic use of vitamin B5 includes its moisturizing effect which relieves itch from poison ivy and rashes etc.
PANTOTHENIC ACID DEFICIENCY SYMPTOMS:
1. Hypercholesterolemia:
Exhaustion with no apparent reason is an indicator of high cholesterol particularly the bad cholesterol. Vitamin B5 performs the role of replenishing the energy stores. In addition, the stable form of Pantothenic acid, Pantethine is believed to aid the transport of fats by the oxidation of fatty acids which reduces the blood cholesterol level. It has been said that pantothenic acid facilitates conversion of HDL cholesterol to LDL cholesterol thus improving the blood flow through arteries and ultimately the health conditions. During continual deficiency of Pantothenic acid, hypercholesterolemia may aggravate to symptoms of angina, stroke, heart attack and even corneal arcus.
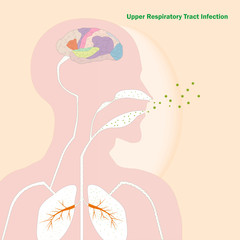
2. Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Pantothenic acid is effective for treating respiratory conditions such as cough, cold, asthma and other bronchial problems. Referring to its antioxidant characteristic, it is reliable to reduce inflammation and thus promote wound healing. Liver function is also boosted by Vitamin B5 since the coenzyme A formed by B5 is effective in removing the toxins from the liver. Inadequacy of pantothenate leads to low resistance towards upper respiratory tract infections.
3. Gastrointestinal discomforts:
Vitamin B5 has the ability to relieve constipation by stimulating muscle contraction and aiding the passage of stool through intestine. Its part in promoting healthy digestion of food and absorption of other vitamins allows one to improve his/ her nutritional level. Insufficiency of Pantothenic acid leads to symptoms such as vomiting, stomach pain, cramps, heartburn, nausea and loss of apatite. Skin problems such as itches, dryness, infections and alopecia may also arise as the nourishment of the epithelium is affected. Vitamin B5 also has a moisturizing effect on the skin.

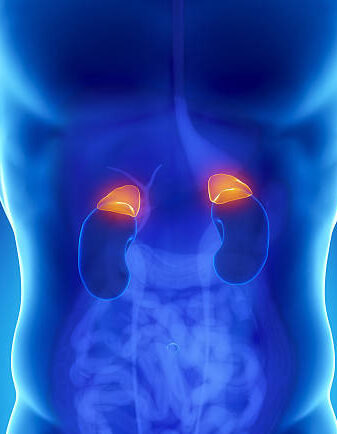
4. Adrenal Problems:
Pantothenic acid is indirectly responsible for the synthesis of the sex and stress related hormones by the production of fatty acids required to make them. The adrenal glands are the pyramid shaped structures lying over the kidneys where the hormones are formed. Adrenal insufficiency is the insensitivity of adrenal cortex to ACTH which is released from posterior pituitary to stimulate the secretion of adrenal hormones. Deficiency of B5 leads to severe headaches, anxiety, depression and even neuronal damage as the body’s natural fight or flight response to stressful situations is terminated. Infertility is also a major issue along with fatigue and muscle weakness.
5. Burning Foot Syndrome:
The symptoms of hot and painful feet with aching, pins and needles sensation and numbness in feet and legs are associated with Burning Foot Syndrome. The disease is a manifestation of underlying peripheral neuropathy which in this case is the result of nutritional imbalances. The scarcity of Pantothenic acid damages the peripheral sensory nerves that directly transmit sensory information from the body to the central nervous system. A complete blood count may provide a clear picture of nutritional deficit or any other underlying cause. Nerve function test such as electromyography can assist the diagnosis as well. Supplementation or dietary changes are fruitful in the eradication of disease.

Vulnerable groups for B5 deficiency:
- Women on contraceptives or people taking drugs such as antacids, alcohol etc.
- People with digestive disorders who suffer impaired absorption of vitamin
- People who have increased excretion such as those who have Diabetes Mellitus or are on Hemodialysis.
Dietary sources:
Animal liver, kidney, eggs, yeast, cereals, legumes, milk etc. This vitamin has the most wide distribution found in plants and animals.
Recommended Daily Allowance:
Body requirement of pantothenic acid is dependent upon the total caloric intake of the adult person. Hence, for adults : 5-24 mg/2500 calories , for children 5 mg. Increased demand during stress, pregnancy and lactation, convalescence, burns, antibiotic therapy, growing children.
Over dose safety of Pantothenic acid is subjected to its water soluble nature which causes its excretion in urine. However, too much Vitamin B5 may lead to diarrhea. It is heat sensitive and so boiling and deep frying the food leads to loss of B5 content.
One response to “5 signs you have Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) deficiency!”
[…] 5 signs you have Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) deficiency! […]